Genesis 1:11 And God said, “Let the earth sprout vegetation, plants yielding seed, and fruit trees bearing fruit in which is their seed, each according to its kind, on the earth.” And it was so.
Genesis 1:21 So God created the great sea creatures and every living creature that moves, with which the waters swarm, according to their kinds, and every winged bird according to its kind. And God saw that it was good.
Genesis 1:24 And God said, “Let the earth bring forth living creatures according to their kinds— livestock and creeping things and beasts of the earth according to their kinds.” And it was so.
Genesis 1:27 So God created man in his own image, in the image of God he created him; male and female he created them. And God blessed them. And God said to them, “Be fruitful and multiply and fill the earth and subdue it…”

Discussion
According to its kind
The signature of design in biology is the “according to its kind” for plants, sea creatures, birds and beasts of the earth as recorded in Genesis chapter one. The hallmark of design, in general, is the creation of systems for specific domains and purposes. A Vehicle designed to travel via roads will be significantly different from a vehicle designed to travel in space. Even if some of the materials and subsystems are similar, the overall design of each is governed by the intended use and the environment in which each vehicle operates.

Biology is the same. Creatures are literally designed for specified roles within ecosystems, but you may wonder, if that is true why do we see variations within each kind? Incredibly, the variability of each kind is actually a part of the original design. Variations are often the result of different allele frequencies (1) across distinct creatures within a kind. Mutations of DNA can be a source of variation, but, as often happens, mutations that are “adaptive” result in a reduced robustness for the creature. Sickle Cell Anemia (2) is an example where malarial resistance is offset by reduced blood circulation and the associated medical issues. There are other sources of variability, but they go beyond the scope of this discussion.

The Bauplan and Epigenetics
If mutations of DNA are a source of variation in creatures, why can’t that eventually result in entirely new creatures? There are two primary reasons why there are limits to the amount of variation that creatures can experience due to mutations. One reason is that DNA alone is not the only factor that determines the formation of specific creatures.
DNA is not, in itself, a control mechanism. DNA is simply a repository of information, like a set of files in an office, or drawings stored on a computer. Those files or drawings, by themselves, don’t control or result in anything being produced. Rather, there is an entire production complex that is required, and the nature of that complex will govern what can be produced. For example, spacecraft are not built in a factory that is designed to build automobiles. The requirements for building spacecraft are significantly different from those of automobiles. Consequently, it is important that the information for building automobiles is stored and used in a factory designed to build automobiles.

The same is true for biology. Each kind of creature has what is called a Body Plan or Bauplan (German) (3) which is effectively the common elements for a “factory” for building the creature with that DNA. Closely associated with the Bauplan is the concept of epigenetics (4), which are heritable traits, or a stable change of cell function, that happen without changes to the DNA sequence, and is governed by conditions “outside” or “above” the information contained in the DNA. During embryological development this can even include conditions which the “mother” experiences. Taken together, DNA, the Bauplan and epigenetics are specifically why dogs beget dogs, cats beget cats, and birds beget birds.
Mendelian Genetics
Mendelian genetics (5) was the death knell of Darwinian evolution. Even the evolutionists agreed because they formulated the neo-Darwinian form of evolution (6) early in the twentieth century.
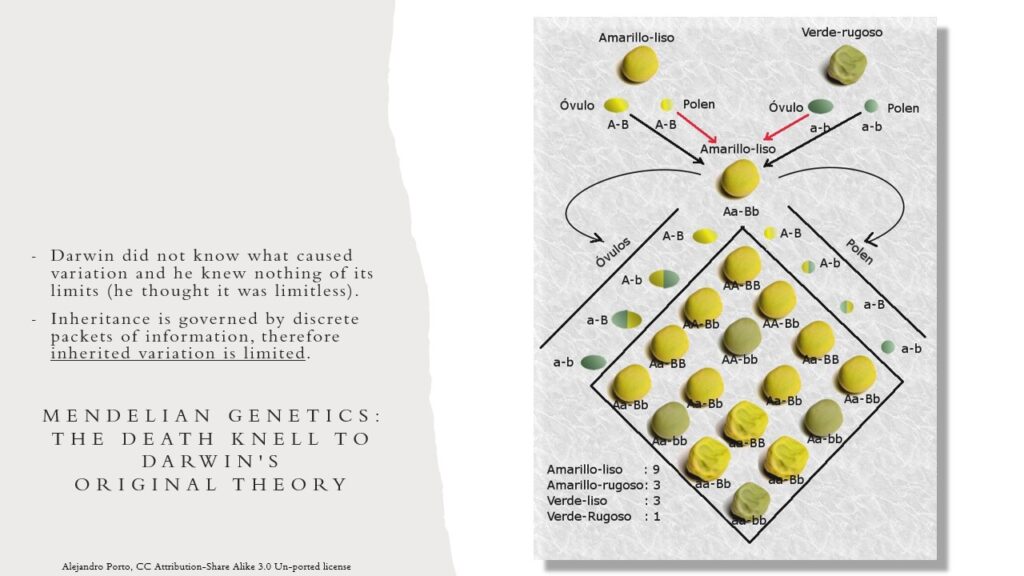
Darwin had no idea what the source of the variations were that he observed, and he fundamentally thought that creatures were “infinitely” elastic, or changeable. But just like a rubber band that is stretched too far and breaks, there is a breaking point for species that are “stretched” by too many mutations. The term for this condition is called Genetic Entropy (7), and all creatures are subject to the limits imposed by entropy. Genetic Entropy not only degrades an entire species, but every individual creature directly experiences the effect of genetic entropy. Whenever cells divide or are replace the new cell will typically experience two or three mutations. Since these mutations continue to buildup over time, as the creature ages, these mutations become a fundamental physical driver of death for that creature (7).
Genetic Entropy

Just as Mendelian genetics was the death knell of Darwinian evolution, genetic entropy is the death knell of neo-Darwinian evolution, and there really is no other contender to take on the mantle of natural evolution to explain the existence of the great variety of creatures apart from special creation.

Without going into too much detail, the issue with mutations is that the effect of a mutation (assuming there is a positive effect) at the organism level is usually too muted by other factors related to survival of individual organisms to effectively select the one or few organisms that have experienced a beneficial mutation. In other words, for the vast majority of creatures the governing factor in the survival sweepstakes for individual creatures of any given species isn’t the much vaunted “Survival of the Fittest,” but rather the real winners are often determined by the “Survival of luckiest.” Oddly enough, if random chance is the source of many mutations, it turns out that random chance, i.e. “random selection,” is also the governing factor in survival, and “random selection” generally cancels out the effect of any randomly generated beneficial mutations.

The other, even more significant factor, is that the vast majority of mutations are deleterious to the robustness, and thus the survival, of any single creature and ultimately the species. You might think that a harmful mutation would be selected out as a sort of “De-selection of the weak” principle. However, the vast majority of mutations are only slightly deleterious, so that, rather than forcing a de-selection of the creature with the bad mutations via a positive selection of the “slightly” better organisms, the slightly deleterious mutations of any single creature have little or no impact on the survival of that creature, so consequently the slightly negative mutations slowly accumulate over many generations across the entire genome of a species. Since every individual creature of a species experiences an accumulation of slightly different deleterious mutations, every member of a species effectively deteriorates concurrently with all other creatures of its generation. Even if “slightly” better organisms existed just a few generations ago, they have all died and no longer exist to be selected in order to maintain the robustness of the species.
There is one final issue involving beneficial mutations, which is that real benefit or “improvement” almost always requires multiple simultaneous mutations of independent genes. For example, what if there was a mutation of the blood cells that would enable the hemoglobin to transport more oxygen and remove more carbon dioxide from tissues? That might convey a real advantage in stamina, strength, and overall health. However, what if the size of the new hemoglobin molecule had to grow by 50% to enable that greater transport capability? It turns out that the smallest capillaries are literally just large enough to pass a single hemoglobin, therefore, the genes that govern the size of capillaries would also have to mutate to enable the larger hemoglobin to pass unhindered, and that is the problem. The genes for producing hemoglobin and the genes for developing the capillaries are completely independent. If the capillaries don’t get bigger the larger hemoglobin will literally get stuck and the organism might die a cruel death of cell level asphyxiation.
Therein lies the rub for evolution. Organisms are composed of multiple independently governed systems, e.g. circulatory, respiratory, digestive, endocrine, skeletal, etc., that are inter-dependent for proper function of the entire organism. All those systems must be fully functional and coordinated for the organism to survive and thrive. If only one system is “improved,” without a corresponding adjustment in the related systems, the overall entity may be, and likely, will be negatively impacted.

You may wonder why you haven’t heard about genetic entropy, if it is one fact (and there are many such facts) that disproves natural evolution. The answer is both simple and complex. The simple answer is that the majority of schools, educational programs, scientists, museums and doctors know nothing about genetic entropy, or have been told by the “experts,” to pay no attention to genetic entropy which is just another crackpot attack on the “truth” of evolution. That, of course, gets us into the complex problem—people. And on that score, I will say no more here. However, let’s talk about you.
What, or who, are you going to believe?
Do you believe the “experts?” On many, many things it is wise to believe the experts because they are educated and experienced, but on some things, you should believe what your own God-given intelligence and logic is telling you, because we are talking about your future and your well-being, and not just for now, but also for eternity. Choose wisely.
References:
(1) Allele Frequency: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Allele_frequency
(2) Sickle cell disease: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Sickle_cell_disease
(3) Bauplan: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Body_plan
(4) Epigenetics: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Epigenetics
(5) Mendelian inheritance: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Mendelian_inheritance
(6) Neo- Darwinism: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Neo-Darwinism
(7) Genetic Entropy: Genetic Entropy also, the book by the same name